Introduction
What is AI?
- Systems that think like humans
- Systems that act like humans
- Systems that think rationally
- Systems that act rationally
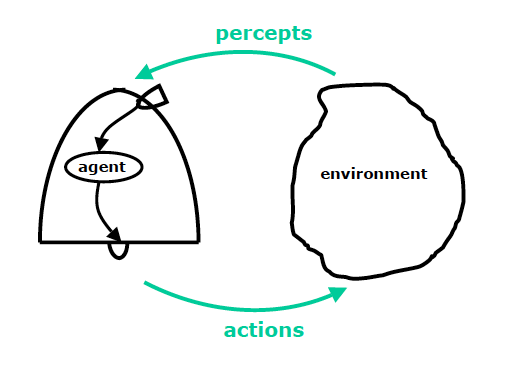
Agents
Software that gathers information about an environment and takes actions based on that information.
Ex
- a robot
- a web shopping program
- a traffic control system
World Model
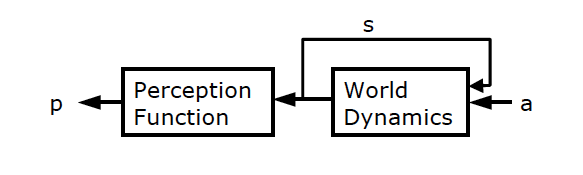
S × A → S
| 代號 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| A | the action space (through actuators) |
| P | the percept space (by sensors) |
| E | the environment: A* → P |
| S | internal state (may not be visible to agent) |
Rationality
A rational agent takes actions it believes will achieve its goals – Do the right things
- No need to know everything
- No need to be successful for other reasons
- Just do the right things, given what they know and what they want to achieve
Ex
| 說明 | rational or not | 備註 |
|---|---|---|
| Assume I don’t like to get wet, so I always bring an umbrella | No | |
| Depends on the weather forecast and whether I’ve heard it. If I’ve heard the forecast for rain (and I believe it) then bringing the umbrella is ____. | Yes | |
| Assume the most recent forecast is for rain but I did not listen to it and I did not bring my umbrella. Is that rational? | Yes since I did not know about the recent forecast! | Rationality ≠ omniscience, clairvoyance |
| Suppose there’ll be no rain according to the forecast, but still, I bring my umbrella, and I happen to use it to defend myself against an attack. Is that rational? | No, despite successful defense, yet it was done for the wrong reason. | Rationality ≠ success |
Limited Rationality
The agent might not be able to compute the best action. So, we want to use limited rationality: acting in the best way you can subject to the computational constraints that you have